Camel K in Tekton Pipelines
Introduction
| Available from Camel K 1.8.0 |
Camel K can be directly used in Tekton Pipelines tasks since it’s container image ships the kamel CLI tool, that
can be used to create all needed resources by interacting with the Kubernetes cluster.
For example, the following Tekton pipeline task can be used to run an integration:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: camel-k-run-integration
spec:
inputs:
resources:
- name: repository
type: git
params:
- name: file
description: The integration file to run
steps:
- name: run-integration
image: docker.io/apache/camel-k:1.8.0 (1)
workingDir: /workspace/repository
command:
- kamel
args:
- "run"
- "--wait"
- "$(inputs.params.file)" (2)| 1 | The base image for the step is apache/camel-k:1.8.0 |
| 2 | It executes command kamel run --wait ${inputs.params.file}, with file to run received as parameter |
When executed, such task creates an integration resource from the given file (which is supposed to be contained in the input git repository) and waits for the integration to be fully running before completing.
This task is a building block for more complex scenarios that can be composed in Tekton pipelines. If you want to learn more, just follow the remainder of the tutorial.
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes the following requirements are met:
-
OpenShift (or OKD) 4+ cluster (works also on "vanilla" Kubernetes with some adjustment) and
ocbinary tool -
Tekton Pipelines 0.5.2 (different versions may need adjustments)
-
Camel K Client Tools 1.0.0-M2 (
kamelbinary tool)
Cluster Setup
This tutorial assumes that Tekton Pipelines are already installed in the cluster. Refer to the Tekton documentation to learn how to install them.
Camel K cluster resources need to be installed on the cluster:
# Use the oc tool to login as cluster admin to the target cluster, then
kamel install --cluster-setupThis will install the Camel K CRD (custom resource definitions) and roles to access them. You can switch to a standard user after doing this operation.
Creating the Pipeline
We’re going to create a pipeline on a new namespace. The first step is to create the namespace:
oc new-project camel-pipelinesSetting up a ServiceAccount
Any running container that needs to interact with the Kubernetes API (in our case, to create deployment and integration resources) must have special permissions granted to its service account.
Download the camel-k-pipeline-permissions.yaml file and save it into a directory in your hard drive.
Then install it using the oc client tool:
oc apply -f camel-k-pipeline-permissions.yamlThis creates a Kubernetes ServiceAccount named camel-k-pipeline
that is authorized to create the same kind of resources that the Camel K operator needs to create. We’ll use that service account to run our pipeline.
Creating the Pipeline Definition
Let’s now create the pipeline definition. Download the camel-k-pipeline-task-definition.yaml file and apply it to the cluster:
oc apply -f camel-k-pipeline-task-definition.yamlThis creates a series of resources, including a pipeline definition that you can immediately see on the OpenShift developer console.
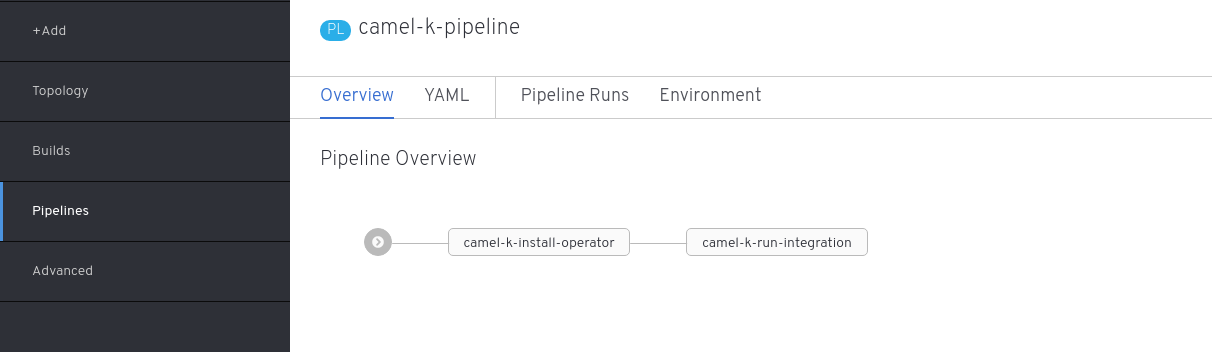
The pipeline just created is composed of two tasks.
The last task (camel-k-run-integration) is the one we’ve already described in the introduction, while the first task just installs the operator in the current namespace.
The definition of the first task is shown in the following excerpt:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: camel-k-install-operator
spec:
steps:
- name: install
image: docker.io/apache/camel-k:1.8.0
command:
- kamel
args:
- "install"
- "--skip-cluster-setup"As you see, it’s just doing a kamel install --skip-cluster-setup (we’ve already done the cluster setup in the preparation phase).
Both tasks are executed in sequence in the pipeline that is shown below.
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: Pipeline
metadata:
name: camel-k-pipeline
spec:
resources:
- name: source-repo
type: git
tasks:
- name: install-operator
taskRef:
name: camel-k-install-operator
- name: run-integration
runAfter: [install-operator]
taskRef:
name: camel-k-run-integration
resources:
inputs:
- name: repository
resource: source-repo
params:
- name: file
value: "examples/tekton/hello.groovy"The integration file to be executed is set to examples/tekton/hello.groovy that is a simple "Hello World" integration contained in the Camel K
github repository example/tekton directory.
In order to specify the actual source repository, the definition file contains also the following resource:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: PipelineResource
metadata:
name: camel-k-examples-git
spec:
type: git
params:
- name: revision
value: main
- name: url
value: https://github.com/apache/camel-kThe repo will be now used as input for the run-integration task in the pipeline.
Triggering a Pipeline Execution
Everything is now ready to be executed and the last thing missing is a trigger. Download the camel-k-pipeline-task-run.yaml file and apply it to the cluster:
oc apply -f camel-k-pipeline-task-run.yamlThe file contains only a PipelineRun resource:
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1alpha1
kind: PipelineRun
metadata:
name: camel-k-pipeline-run-1
spec:
pipelineRef:
name: camel-k-pipeline
serviceAccount: 'camel-k-pipeline' (1)
resources:
- name: source-repo
resourceRef:
name: camel-k-examples-git (2)| 1 | The PipelineRun binds the pipeline to the service account previously created |
| 2 | It also binds the pipeline to the Camel K repository containing the examples |
The creation of the file starts the execution of the pipeline and its progress can be monitored on the OpenShift developer console.
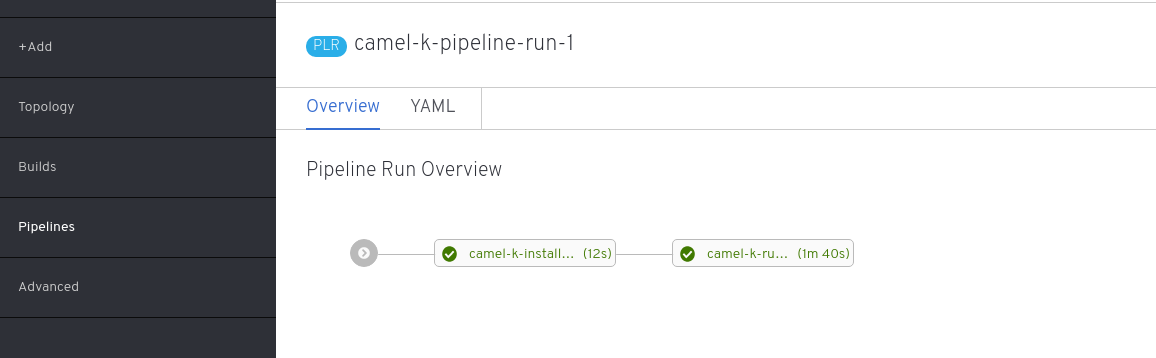
| To execute the PipelineRun again, delete previous runs before re-applying |
The result of the pipeline execution is the Camel K operator and an integration named hello running on the cluster:

There are certainly other ways to trigger an execution of a pipeline, like as reaction to a change in the git repository, but this is left to you as exercise ;)
Refer to the Tekton repository for more information.