Direct VM
Since Camel 2.10
Both producer and consumer are supported
The Direct-Vm component provides direct, synchronous invocation of
any consumers in the JVM when a producer sends a message exchange.
This endpoint can be used to connect existing routes in the same camel
context, as well from other camel contexts in the same JVM.
This component differs from the Direct component in that Direct-VM supports communication across CamelContext instances - so you can use this mechanism to communicate across web applications (provided that camel-core.jar is on the system/boot classpath).
At runtime you can swap in new consumers, by stopping the existing
consumer(s) and start new consumers.
But at any given time there can be at most only one active consumer for
a given endpoint.
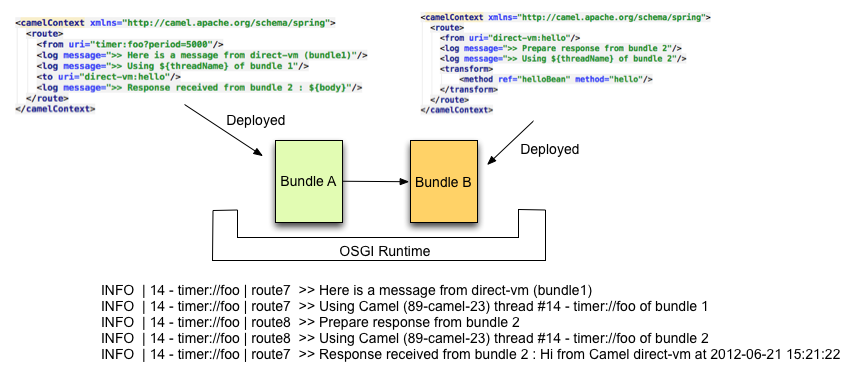
This component allows also to connect routes deployed in different OSGI
Bundles as you can see here after. Even if they are running in different
bundles, the camel routes will use
the same thread. That autorises to develop applications using
Transactions - Tx.
Configuring Options
Camel components are configured on two separate levels:
-
component level
-
endpoint level
Configuring Component Options
The component level is the highest level which holds general and common configurations that are inherited by the endpoints. For example a component may have security settings, credentials for authentication, urls for network connection and so forth.
Some components only have a few options, and others may have many. Because components typically have pre configured defaults that are commonly used, then you may often only need to configure a few options on a component; or none at all.
Configuring components can be done with the Component DSL, in a configuration file (application.properties|yaml), or directly with Java code.
Configuring Endpoint Options
Where you find yourself configuring the most is on endpoints, as endpoints often have many options, which allows you to configure what you need the endpoint to do. The options are also categorized into whether the endpoint is used as consumer (from) or as a producer (to), or used for both.
Configuring endpoints is most often done directly in the endpoint URI as path and query parameters. You can also use the Endpoint DSL as a type safe way of configuring endpoints.
A good practice when configuring options is to use Property Placeholders, which allows to not hardcode urls, port numbers, sensitive information, and other settings. In other words placeholders allows to externalize the configuration from your code, and gives more flexibility and reuse.
The following two sections lists all the options, firstly for the component followed by the endpoint.
Component Options
The Direct VM component supports 7 options, which are listed below.
| Name | Description | Default | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
Allows for bridging the consumer to the Camel routing Error Handler, which mean any exceptions occurred while the consumer is trying to pickup incoming messages, or the likes, will now be processed as a message and handled by the routing Error Handler. By default the consumer will use the org.apache.camel.spi.ExceptionHandler to deal with exceptions, that will be logged at WARN or ERROR level and ignored. |
false |
boolean |
|
If sending a message to a direct endpoint which has no active consumer, then we can tell the producer to block and wait for the consumer to become active. |
true |
boolean |
|
Whether the producer should be started lazy (on the first message). By starting lazy you can use this to allow CamelContext and routes to startup in situations where a producer may otherwise fail during starting and cause the route to fail being started. By deferring this startup to be lazy then the startup failure can be handled during routing messages via Camel’s routing error handlers. Beware that when the first message is processed then creating and starting the producer may take a little time and prolong the total processing time of the processing. |
false |
boolean |
|
The timeout value to use if block is enabled. |
30000 |
long |
|
Whether autowiring is enabled. This is used for automatic autowiring options (the option must be marked as autowired) by looking up in the registry to find if there is a single instance of matching type, which then gets configured on the component. This can be used for automatic configuring JDBC data sources, JMS connection factories, AWS Clients, etc. |
true |
boolean |
|
Sets a HeaderFilterStrategy that will only be applied on producer endpoints (on both directions: request and response). Default value: none. |
HeaderFilterStrategy |
||
Whether to propagate or not properties from the producer side to the consumer side, and vice versa. Default value: true. |
true |
boolean |
Endpoint Options
The Direct VM endpoint is configured using URI syntax:
direct-vm:name
with the following path and query parameters:
Query Parameters (9 parameters)
| Name | Description | Default | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
Allows for bridging the consumer to the Camel routing Error Handler, which mean any exceptions occurred while the consumer is trying to pickup incoming messages, or the likes, will now be processed as a message and handled by the routing Error Handler. By default the consumer will use the org.apache.camel.spi.ExceptionHandler to deal with exceptions, that will be logged at WARN or ERROR level and ignored. |
false |
boolean |
|
To let the consumer use a custom ExceptionHandler. Notice if the option bridgeErrorHandler is enabled then this option is not in use. By default the consumer will deal with exceptions, that will be logged at WARN or ERROR level and ignored. |
ExceptionHandler |
||
Sets the exchange pattern when the consumer creates an exchange. Enum values:
|
ExchangePattern |
||
If sending a message to a direct endpoint which has no active consumer, then we can tell the producer to block and wait for the consumer to become active. |
true |
boolean |
|
Whether the producer should fail by throwing an exception, when sending to a Direct-VM endpoint with no active consumers. |
false |
boolean |
|
The timeout value to use if block is enabled. |
30000 |
long |
|
Sets a HeaderFilterStrategy that will only be applied on producer endpoints (on both directions: request and response). Default value: none. |
HeaderFilterStrategy |
||
Whether the producer should be started lazy (on the first message). By starting lazy you can use this to allow CamelContext and routes to startup in situations where a producer may otherwise fail during starting and cause the route to fail being started. By deferring this startup to be lazy then the startup failure can be handled during routing messages via Camel’s routing error handlers. Beware that when the first message is processed then creating and starting the producer may take a little time and prolong the total processing time of the processing. |
false |
boolean |
|
Whether to propagate or not properties from the producer side to the consumer side, and vice versa. Default value: true. |
true |
boolean |
Samples
In the route below we use the direct component to link the two routes together:
from("activemq:queue:order.in")
.to("bean:orderServer?method=validate")
.to("direct-vm:processOrder");And now in another CamelContext, such as another OSGi bundle
from("direct-vm:processOrder")
.to("bean:orderService?method=process")
.to("activemq:queue:order.out");And the sample using XML DSL:
<route>
<from uri="activemq:queue:order.in"/>
<to uri="bean:orderService?method=validate"/>
<to uri="direct-vm:processOrder"/>
</route>
<route>
<from uri="direct-vm:processOrder"/>
<to uri="bean:orderService?method=process"/>
<to uri="activemq:queue:order.out"/>
</route>Spring Boot Auto-Configuration
When using direct-vm with Spring Boot make sure to use the following Maven dependency to have support for auto configuration:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.camel.springboot</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-directvm-starter</artifactId>
<version>x.x.x</version>
<!-- use the same version as your Camel core version -->
</dependency>The component supports 8 options, which are listed below.
| Name | Description | Default | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
Whether autowiring is enabled. This is used for automatic autowiring options (the option must be marked as autowired) by looking up in the registry to find if there is a single instance of matching type, which then gets configured on the component. This can be used for automatic configuring JDBC data sources, JMS connection factories, AWS Clients, etc. |
true |
Boolean |
|
If sending a message to a direct endpoint which has no active consumer, then we can tell the producer to block and wait for the consumer to become active. |
true |
Boolean |
|
Allows for bridging the consumer to the Camel routing Error Handler, which mean any exceptions occurred while the consumer is trying to pickup incoming messages, or the likes, will now be processed as a message and handled by the routing Error Handler. By default the consumer will use the org.apache.camel.spi.ExceptionHandler to deal with exceptions, that will be logged at WARN or ERROR level and ignored. |
false |
Boolean |
|
Whether to enable auto configuration of the direct-vm component. This is enabled by default. |
Boolean |
||
Sets a HeaderFilterStrategy that will only be applied on producer endpoints (on both directions: request and response). Default value: none. The option is a org.apache.camel.spi.HeaderFilterStrategy type. |
HeaderFilterStrategy |
||
Whether the producer should be started lazy (on the first message). By starting lazy you can use this to allow CamelContext and routes to startup in situations where a producer may otherwise fail during starting and cause the route to fail being started. By deferring this startup to be lazy then the startup failure can be handled during routing messages via Camel’s routing error handlers. Beware that when the first message is processed then creating and starting the producer may take a little time and prolong the total processing time of the processing. |
false |
Boolean |
|
Whether to propagate or not properties from the producer side to the consumer side, and vice versa. Default value: true. |
true |
Boolean |
|
The timeout value to use if block is enabled. |
30000 |
Long |