Message History
Camel supports the Message History from the EIP patterns book.
The Message History from the EIP patterns allows for analyzing and debugging the flow of messages in a loosely coupled system.
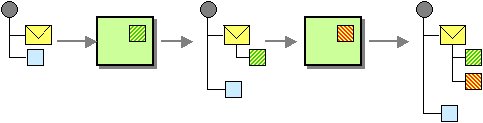
Attaching a Message History to the message will provide a list of all applications that the message passed through since its origination.
Enabling Message History
The message history is disabled by default (to optimize for lower footprint out of the box). You should only enable message history
if needed, such as during development, where Camel can report route stack-traces when a message failed with an exception.
But for production usage, then message history should only be enabled if you have monitoring systems that rely on gathering these
fine-grained details. When message history is enabled then there is a slight performance overhead as the history data is stored
in a java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList due to the need of being thread safe.
The Message History can be enabled or disabled per CamelContext or per route (disabled by default). For example, you can turn it on with:
camelContext.setMessageHistory(true);Or in XML
<camelContext messageHistory="true">
</camelContext>Or when using Spring Boot or Quarkus, you can enable this in the configuration file:
camel.springboot.message-history = trueAnd in Quarkus:
camel.quarkus.message-history = trueRoute level Message History
You can also enable or disable message history per route. When doing this then Camel can only gather message history in the routes where this is enabled, which means you may not have full coverage. You may still want to do this, for example to capture the history in a critical route to help pin-point where the route is slow.
A route level configuration overrides the global configuration.
To enable in Java:
from("jms:cheese")
.messageHistory()
.to("bean:validate")
.to("bean:transform")
.to("jms:wine");You can also turn off message history per route:
from("jms:cheese")
.messageHistory(false)
.to("bean:validate")
.to("bean:transform")
.to("jms:wine");And in XML:
<route messageHistory="true">
<from uri="jms:cheese"/>
<to uri="bean:validate"/>
<to uri="bean:transform"/>
<to uri="jms:wine"/>
</route>Enabling source location information
Camel is capable of gathering precise source file:line-number for each EIPs in the routes. When enabled, then the message history will output this information in the route stack-trace.
To enable source location:
camelContext.setSourceLocationEnabled(true);Or in XML
<camelContext sourceLocationEnabled="true">
</camelContext>Or when using Spring Boot or Quarkus, you can enable this in the configuration file:
camel.springboot.source-location-enabled = trueAnd in Quarkus:
camel.quarkus.source-location-enabled = trueRoute stack-trace in exceptions logged by error handler
If Message History is enabled, then Camel will include this information, when the Error Handler logs exhausted exceptions, where you can see the message history; you may think this as a "route stacktrace".
And example is provided below:
2022-01-06 12:13:06.721 ERROR 67729 --- [ - timer://java] o.a.c.p.e.DefaultErrorHandler : Failed delivery for (MessageId: B4365D4CED3E5E1-0000000000000004 on ExchangeId: B4365D4CED3E5E1-0000000000000004). Exhausted after delivery attempt: 1 caught: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The number is too low
Message History (source location is disabled)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Source ID Processor Elapsed (ms)
route1/route1 from[timer://java?period=2s] 2
route1/setBody1 setBody[bean[MyJavaRouteBuilder method:randomNumbe 0
route1/log1 log 1
route1/filter1 filter[simple{${body} < 30}] 0
route1/throwException1 throwException[java.lang.IllegalArgumentException] 0
Stacktrace
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The number is too low
at sample.camel.MyJavaRouteBuilder.configure(MyJavaRouteBuilder.java:34) ~[classes/:na]
at org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder.checkInitialized(RouteBuilder.java:607) ~[camel-core-model-3.20.0-SNAPSHOT.jar:3.20.0-SNAPSHOT]
at org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder.configureRoutes(RouteBuilder.java:553) ~[camel-core-model-3.20.0-SNAPSHOT.jar:3.20.0-SNAPSHOT]When Message History is enabled then the full history is logged as shown above. Here we can see the full path the message has been routed.
When Message History is disabled (by default) then the error handler logs a brief history with the last node where the exception occurred as shown below:
2022-01-06 12:12:32.072 ERROR 67704 --- [ - timer://java] o.a.c.p.e.DefaultErrorHandler : Failed delivery for (MessageId: CD6D1B185A3706F-0000000000000004 on ExchangeId: CD6D1B185A3706F-0000000000000004). Exhausted after delivery attempt: 1 caught: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The number is too low
Message History (source location and message history is disabled)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Source ID Processor Elapsed (ms)
route1/route1 from[timer://java?period=2s] 2
...
route1/throwException1 throwException[java.lang.IllegalArgumentException] 0
Stacktrace
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The number is too low
at sample.camel.MyJavaRouteBuilder.configure(MyJavaRouteBuilder.java:34) ~[classes/:na]
at org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder.checkInitialized(RouteBuilder.java:607) ~[camel-core-model-3.20.0-SNAPSHOT.jar:3.20.0-SNAPSHOT]
at org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder.configureRoutes(RouteBuilder.java:553) ~[camel-core-model-3.20.0-SNAPSHOT.jar:3.20.0-SNAPSHOT]Here you can see the Message History only outputs the input (route1) and the last step where the exception occurred (throwException1).
Notice that the source column is empty, because source location is not enabled. When enabled then, you can see exactly which source file and line number the message routed:
2022-01-06 12:19:01.277 ERROR 67870 --- [ - timer://java] o.a.c.p.e.DefaultErrorHandler : Failed delivery for (MessageId: 37412D6F722F679-0000000000000003 on ExchangeId: 37412D6F722F679-0000000000000003). Exhausted after delivery attempt: 1 caught: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The number is too low
Message History
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Source ID Processor Elapsed (ms)
MyJavaRouteBuilder:29 route1/route1 from[timer://java?period=2s] 10
MyJavaRouteBuilder:32 route1/setBody1 setBody[bean[MyJavaRouteBuilder method:randomNumbe 1
MyJavaRouteBuilder:33 route1/log1 log 1
MyJavaRouteBuilder:34 route1/filter1 filter[simple{${body} < 30}] 0
MyJavaRouteBuilder:35 route1/throwException1 throwException[java.lang.IllegalArgumentException] 0
Stacktrace
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: The number is too low
at sample.camel.MyJavaRouteBuilder.configure(MyJavaRouteBuilder.java:34) ~[classes/:na]
at org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder.checkInitialized(RouteBuilder.java:607) ~[camel-core-model-3.20.0-SNAPSHOT.jar:3.20.0-SNAPSHOT]
at org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder.configureRoutes(RouteBuilder.java:553) ~[camel-core-model-3.20.0-SNAPSHOT.jar:3.20.0-SNAPSHOT]In this case we can see its the MyJavaRouteBuilder class on line 35 that is the problem.
Configuring route stack-trace from error handler
You can turn off logging Message History with logExhaustedMessageHistory
from the Error Handler using:
errorHandler(defaultErrorHandler().logExhaustedMessageHistory(false));The Error Handler does not log the
message body/header details (to avoid logging sensitive message body details).
You can enable this with logExhaustedMessageBody on the error handler as shown:
errorHandler(defaultErrorHandler().logExhaustedMessageBody(true));In XML configuring this is a bit different, as you configure this in the redeliveryPolicy
of the <errorHandler> as shown:
<camelContext messageHistory="true" errorHandlerRef="myErrorHandler" xmlns="http://camel.apache.org/schema/spring">
<errorHandler id="myErrorHandler">
<redeliveryPolicy logExhaustedMessageHistory="false" logExhaustedMessageBody="true"/>
</errorHandler>
<route>
<from uri="jms:cheese"/>
<to uri="bean:validate"/>
<to uri="bean:transform"/>
<to uri="jms:wine"/>
</route>
</camelContext>MessageHistory API
When message history is enabled during routing Camel captures how the Exchange is routed,
as an org.apache.camel.MessageHistory entity that is stored on the Exchange.
On the org.apache.camel.MessageHistory there is information about the
route id, processor id, timestamp, and elapsed time it took to process the Exchange by the processor.
You can access the message history from Java code:
List<MessageHistory> list = exchange.getProperty(Exchange.MESSAGE_HISTORY, List.class);
for (MessageHistory history : list) {
System.out.println("Routed at id: " + history.getNode().getId());
}